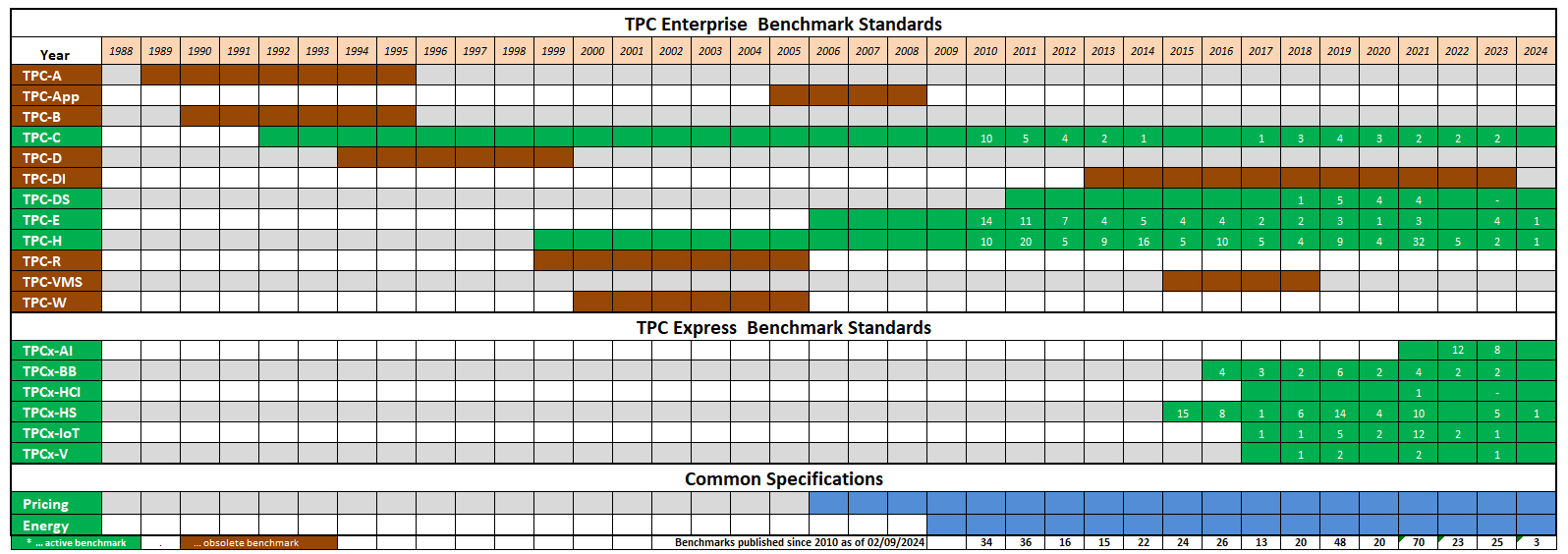
| TPC Benchmarks Overview |
Active TPC Benchmarks |
|
TPC-C
TPC-C simulates a complete computing environment where a population of users executes transactions against a database. The benchmark is centered around the principal activities (transactions) of an order-entry environment. These transactions include entering and delivering orders, recording payments, checking the status of orders, and monitoring the level of stock at the warehouses. While the benchmark portrays the activity of a wholesale supplier, TPC-C is not limited to the activity of any particular business segment, but, rather represents any industry that must manage, sell, or distribute a product or service.TPC-C involves a mix of five concurrent transactions of different types and complexity either executed on-line or queued for deferred execution. It does so by exercising a breadth of system components associated with such environments, which are characterized by:
|
| |
|
TPC-DI
Data Integration (DI), also known as ETL, is the analysis, combination, and transformation of data from a variety of sources and formats into a unified data model representation. Data Integration is a key element of data warehousing, application integration, and business analytics. |
| |
|
TPC-DS
TPC-DS is the de-facto industry standard benchmark for measuring the performance of decision support solutions including, but not limited to, Big Data systems.
The current version is v2. It models several generally applicable aspects of a decision support system, including queries and data maintenance.
Although the underlying business model of TPC-DS is a retail product supplier, the database schema, data population,
queries, data maintenance model and implementation rules have been designed to be broadly representative of modern decision support systems. This benchmark illustrates decision support systems that:
|
| |
|
TPC-E
TPC Benchmark™ E (TPC-E) is a new On-Line Transaction Processing (OLTP) workload developed by the TPC. The TPC-E benchmark uses a database to model a brokerage firm with customers who generate transactions related to trades, account inquiries, and market research. The brokerage firm in turn interacts with financial markets to execute orders on behalf of the customers and updates relevant account information.
The benchmark is “scalable,” meaning that the number of customers defined for the brokerage firm can be varied to represent the workloads of different-size businesses. The benchmark defines the required mix of transactions the benchmark must maintain. The TPC-E metric is given in transactions per second (tps). It specifically refers to the number of Trade-Result transactions the server can sustain over a period of time. Although the underlying business model of TPC-E is a brokerage firm, the database schema, data population, transactions, and implementation rules have been designed to be broadly representative of modern OLTP systems. |
| |
|
TPC-H
The TPC Benchmark-H (TPC-H) is a decision support benchmark. It consists of a suite of business oriented ad-hoc queries and concurrent data modifications. The queries and the data populating the database have been chosen to have broad industry-wide relevance. This benchmark illustrates decision support systems that examine large volumes of data, execute queries with a high degree of complexity, and give answers to critical business questions.The performance metric reported by TPC-H is called the TPC-H Composite Query-per-Hour Performance Metric (QphH@Size), and reflects multiple aspects of the capability of the system to process queries. These aspects include the selected database size against which the queries are executed, the query processing power when queries are submitted by a single stream, and the query throughput when queries are submitted by multiple concurrent users. The TPC-H Price/Performance metric is expressed as $/QphH@Size. |
| |
|
TPC-VMS
The TPC-Virtual Measurement Single System Specification (TPC-VMS) leverages the TPC-C, TPC-E, TPC-H and TPC-DS Benchmarks by adding the methodology and requirements for running and reporting performance metrics for virtualized databases. The intent of TPC-VMS is to represent a Virtualization Environment where three database workloads are consolidated onto one server. Test sponsors choose one of the four benchmark workloads (TPC-C, TPC-E, TPC-H, or TPC-DS) and runs one instance of that benchmark workload in each of the 3 virtual machines (VMs) on the system under test. The 3 virtualized databases must have the same attributes, e.g. the same number of TPC-C warehouses, the same number of TPC-E Load Units, or the same TPC-DS or TPC-H scale factors. The TPC-VMS Primary Performance Metric is the minimum value of the three TPC Benchmark Primary metrics for the TPC Benchmarks run in the Virtualization Environment. |
| |
|
TPCx-BB
TPCx-BB is an Express Benchmark to measure the performance of Hadoop based Big Data systems systems. It measures the performance of both hardware and software components by executing 30 frequently performed analytical queries in the context of retailers with physical and online store presence. The queries are expressed in SQL for structured data and in machine learning algorithms for semi-structured and unstructured data. The SQL queries can use Hive or Spark, while the machine learning algorithms use machine learning libraries, user defined functions, and procedural programs. |
| |
|
TPCx-HS
Big Data technologies like Hadoop have become an important part of the enterprise IT ecosystem. TPC Express Benchmark(tm)HS (TPCx-HS) was developed to provide an objective measure of hardware, operating system and commercial Apache Hadoop File System API compatible software distributions, and to provide the industry with verifiable performance, price-performance and availability metrics. The benchmark models a continuous system availability of 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. |
| |
|
TPCx-V
The TPCx-V benchmark was developed to measure the performance of servers running database workloads in virtual machines. It has a publicly available, end-to-end benchmarking kit that simulates the multi-tenancy phenomena of elasticity, capacity planning, and load variation in cloud data centers. This kit was developed completely from scratch in Java and C++ with PostgreSQL as the target database. |
| |
| Supporting TPC Benchmarks |
|
TPC-Energy
The TPC-Energy Specification contains the rules and methodology for measuring and reporting an energy metric in TPC Benchmarks. This includes the energy consumption of system components associated with typical business information technology environments, which are characterized by:
The measuring and publishing of the TPC-Energy Metrics in the TPC Benchmarks are optional and are not required to publish a TPC Result. |
| |
|
TPC-Pricing
The TPC Pricing Subcommittee was chartered to recommend revisions to the existing pricing methodology so that prices used in published TPC results are verifiable. In the course of this activity, a decision was made to develop a single pricing specification that is consistent for all TPC benchmark. |
|
Pricing Guidelines |